Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth is more than a marketing hook; it marks a real shift in how lean teams operate, compete, and scale. Across industries, affordable digital tools for SMBs empower startups to streamline operations and deliver faster value. Cloud computing removes hardware hurdles, while automation handles repetitive tasks, freeing time for strategic growth. Data analytics turns raw data into actionable insights, guiding decisions that improve the customer experience. By combining these elements, small businesses can compete more effectively and pursue sustainable growth.
In other words, this phenomenon represents a modern tech stack for growth that goes beyond gadgets. For smaller enterprises, cloud-based platforms, automation workflows, and data-driven insights form a cohesive engine that boosts efficiency, foresight, and engagement. You might hear it described as digital transformation for small firms, an optimized toolkit for SMBs, or growth enablement through intelligent operations. The aim is to translate technology into repeatable wins—faster onboarding, smarter marketing, and better customer relationships—by blending scalable infrastructure with practical, measurable initiatives.
1) Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth: Pillars, Tools, and Practical Steps
Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth is not a single gadget; it’s an integrated approach that combines digital tools for SMBs, cloud-based applications, automation, and data-driven insights to create a scalable growth engine. Lean teams can compete more effectively when these elements work together to streamline operations, illuminate decisions, and elevate the customer experience. By framing growth around efficiency, insight, and experience, small businesses can unlock opportunities that previously seemed out of reach.
The core idea is to build a practical tech stack rather than chase every new feature. Start with a focused selection of digital tools for SMBs that address your top bottlenecks, then layer in cloud computing, automation, and data analytics. When these pillars converge, you gain faster decision-making, fewer manual errors, and a stronger platform for sustainable expansion that also supports a superior customer experience.
2) Digital tools for SMBs: From CRM to E-Commerce and Beyond
Digital tools for SMBs span CRM, marketing automation, invoicing, project management, and e-commerce platforms. These tools help small teams coordinate work, gain visibility, and deliver consistent results without overwhelming resources. A modern CRM centralizes contacts and interactions, enabling better lead management and forecasting that align marketing with sales efforts.
Marketing automation, scalable invoicing, and cloud-based collaboration tools turn repetitive tasks into repeatable processes. By implementing a focused pilot—perhaps automating lead nurturing or streamlining invoicing cycles—you can quantify gains in engagement, accuracy, and cycle time before expanding the rollout across the organization.
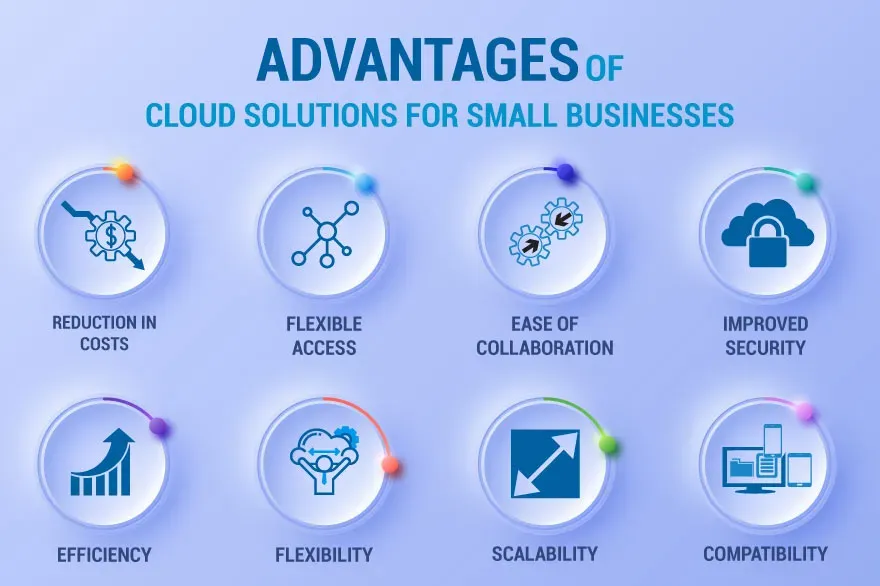
3) Cloud Computing: A Growth Accelerator for Small Teams
Cloud computing provides scalable infrastructure and software delivery that eliminates large upfront hardware costs. For small businesses, cloud-based solutions enable remote collaboration, flexible access to apps, and predictable usage-based pricing. This translates into real-time data sharing, multi-user work streams, and improved disaster recovery—critical capabilities as you scale.
To leverage cloud computing, map your most critical workloads—such as CRM, accounting, inventory, and e-commerce—to cloud-based solutions and execute a phased migration plan. Emphasize data security, governance, clear access controls, and robust backups to minimize downtime while maintaining agility as your team grows.
4) Automation and AI: Elevating Efficiency and Customer Operations
Automation and AI are about augmenting human work, not replacing people. By automating repetitive workflows, customer service routines, marketing actions, and data processing, small businesses create a leaner operation with faster execution. This enables teams to focus on higher-value activities that drive growth and customer value.
Examples of impact include marketing automation that personalizes outreach, robotic process automation for reconciliation and reporting, chatbots that handle routine inquiries, and inventory automation that reduces stockouts. When implementing automation, begin with high-impact processes, design for auditability, and ensure staff understand how automation supports their roles rather than replacing them.
5) Data Analytics: Turning Data into Growth Signals for SMBs
Data analytics bridges raw information and informed decisions. For small businesses, analytics translate everyday operations into measurable insights—from ROI by channel to product profitability and churn drivers. Well-planned analytics help leaders set meaningful KPIs and turn data into action across departments.
Practical steps include defining KPIs such as revenue growth rate, customer lifetime value, CAC, and order fulfillment times; building simple dashboards; and integrating data from sales, marketing, support, and finance. The goal is to create an actionable feedback loop that tests hypotheses, optimizes campaigns, and allocates resources to the most impactful growth initiatives.
6) Customer Experience: Tech-Driven Approaches to Loyalty and Revenue
Customer experience is the sum of every touchpoint a customer has with your business. Technology enhances this experience by enabling faster responses, personalized recommendations, and consistent service across channels. A strong focus on customer experience aligns growth with retention and advocacy.
Key enhancements include personalization, omnichannel support, and real-time feedback loops that guide product and service improvements. By delivering seamless interactions, you boost lifetime value, encourage repeat purchases, and generate positive word-of-mouth—outcomes especially valuable for small businesses with limited marketing budgets. A disciplined, pilot-driven approach helps you scale these improvements without overwhelming your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth and why is it relevant for SMBs?
Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth refers to using an integrated mix of digital tools for SMBs—cloud computing, automation, data analytics, and a customer-experience focus—to grow efficiently. It helps lean teams operate more effectively, gain practical insights, and deliver better service without large-scale investments. By combining these technologies, small businesses can compete, scale, and improve profitability.
How can digital tools for SMBs and cloud computing accelerate growth on a limited budget?
Cloud computing enables scalable, pay-as-you-go access to apps and services, reducing upfront hardware costs. Digital tools for SMBs like CRM, marketing automation, and invoicing streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and accelerate decision-making, helping you grow revenue and improve efficiency without breaking the bank.
In what ways can automation and AI contribute to growth for small businesses?
Automation and AI elevate human work by handling repetitive tasks, speeding workflows, and providing smarter insights. Use automation for marketing actions, customer support, and back-office processes; apply AI to forecast demand and optimize pricing. Start with high-impact, repeatable processes and ensure changes are auditable and aligned with teams.
What role does data analytics play in turning data into growth for small businesses?
Data analytics translates raw data into measurable growth insights. Define KPIs (e.g., CAC, LTV, revenue growth), build simple dashboards, and integrate data from sales, marketing, and finance to reveal cross-functional opportunities. Use these insights to optimize campaigns, pricing, and operations.
How can improving customer experience with technology drive growth for small businesses?
Technology enhances customer experience through personalization, omnichannel support, and real-time feedback. By delivering seamless interactions and tailored recommendations, you can boost retention and lifetime value, while feedback loops inform continuous improvement across channels.
What practical steps should SMBs take to implement these technologies effectively?
Follow a practical, phased plan: 1) Assess and align processes with growth goals and identify impactful tools; 2) Run 90-day pilots for one or two projects; 3) Establish governance, security, and ownership; 4) Train staff and socialize workflows; 5) Measure KPI impact and iterate. This approach leverages digital tools for SMBs, cloud computing, automation, and data analytics to build a scalable growth engine.
| Key Point | What It Means | Primary Benefit | Practical Tips / Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital tools for SMBs | A suite of software applications that streamline sales, marketing, operations, and finance (e.g., CRM, marketing automation, invoicing, accounting, project management, e-commerce). | Faster decision-making, fewer manual errors, and greater capacity to scale. | Start with a focused pilot to address a bottleneck (e.g., lead follow-up or invoicing); measure impact before broader adoption. Examples: implement a modern CRM, marketing automation, cloud accounting, and integrated project management. |
| Cloud computing | Scalable infrastructure and software delivery via the cloud, enabling remote work and flexible access to applications. | Scalability, accessibility, cost control, and security/compliance. | Map critical workloads (CRM, accounting, inventory) to cloud solutions; plan phased migrations; establish access controls and backups; prioritize security and governance. |
| Automation and AI | Automating repetitive tasks and using AI to support decision-making and operations (e.g., workflows, data processing, customer interactions). | Elevates human work, improves efficiency, and speeds execution. | Examples include marketing automation workflows, robotic process automation (RPA), chatbots/virtual assistants, and inventory/order processing automation; start with high-impact processes and ensure auditable, adjustable setups. |
| Data analytics | Turning raw data into actionable insights; tracking performance across channels and operations; building dashboards; integrating data from multiple sources. | Informed decisions, measurable growth, cross-functional insights. | Define KPIs (revenue growth rate, LTV, CAC, gross margin, order fulfillment), create simple dashboards, and combine data from sales, marketing, support, and finance to reveal actionable insights. |
| Customer experience | Technology-enabled interactions that improve service quality and consistency across channels; personalization and timely communication. | Higher retention, increased lifetime value, and stronger word-of-mouth referrals. | Focus on personalization, omnichannel support, and real-time feedback loops to guide product and service improvements. |
| Implementation strategies (phased) | A practical, phased approach to adopting technology that minimizes disruption and maximizes ROI. | Better ROI, lower risk, and smoother adoption across the organization. | Step 1: Assess and align processes and goals; Step 2: Prioritize pilots; Step 3: Establish governance; Step 4: Train and socialize; Step 5: Measure and iterate; use a test-and-learn mindset to scale successful pilots. |
| Measuring growth and momentum | Track progress by connecting technology investments to outcomes; maintain near real-time visibility. | Sustained momentum and continuous improvement. | Define and monitor dashboards for metrics like revenue growth rate, gross margin, CAC, LTV, repeat purchase rate, and customer satisfaction; focus on trajectory and multi-metric trends rather than any single metric. |
Summary
Conclusion: Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth is no longer a distant dream but a practical, accessible pathway to sustained expansion. By embracing digital tools for SMBs, cloud computing, automation, data analytics, and a customer-centric experience, small businesses can streamline operations, unlock new revenue streams, and deliver meaningful value to customers. The true strength lies in an integrated tech stack that coordinates these elements—piloting first, measuring impact, and scaling what works. With deliberate planning, governance, and a data-informed mindset, Technology Transforming Small Businesses for Growth becomes an achievable reality for organizations of all sizes.