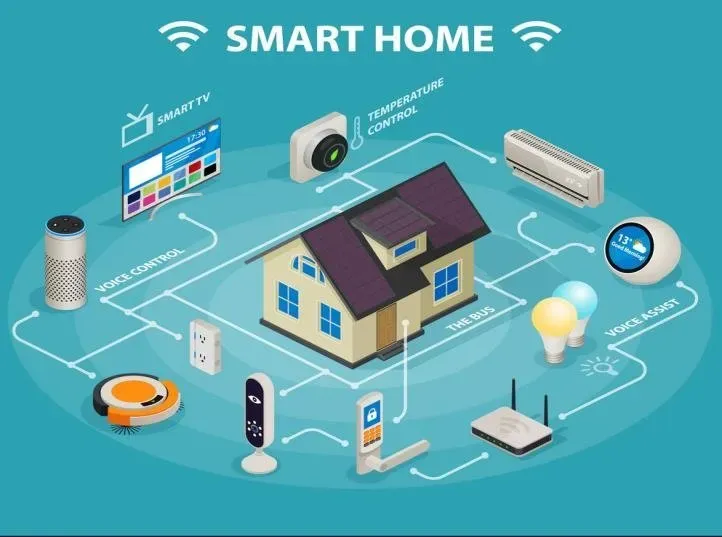
Smart Homes and IoT are no longer a distant dream but a practical reality that can transform how we live, work, and relax at home. At its core, IoT home automation connects sensors, devices, and apps through a centralized system, enabling seamless control and smarter daily routines. From energy efficiency with IoT to home automation benefits like convenience and safety, smart home devices can dim lights at sunset, learn your comfort preferences, and alert you to unusual activity. This guide explores the core components and practical steps to build a connected living environment that genuinely improves everyday life. By focusing on compatibility and user experience, you can start with a small setup and scale to a cohesive system.
In other words, the same idea is realized through internet-connected homes and intelligent ecosystems that automate routines and optimize energy use. A broad range of devices—sensors, cameras, thermostats, and smart appliances—work together via hubs, platforms, and standards that make the experience intuitive rather than fragmented. LSI-friendly terms such as smart home technology, home automation systems, and IoT-enabled living spaces help search engines understand the topic while readers encounter familiar language. The emphasis remains on practical benefits like convenience, safety, cost savings, and accessibility, all achieved through thoughtful integration and ongoing intelligence.
Smart Homes and IoT: Building a Connected Living Environment
Smart Homes and IoT have moved from a futuristic promise to a practical reality that shapes how we live, work, and relax. In a connected living setup, devices and sensors communicate with each other and with you through a centralized system, turning everyday tasks into smooth, automated routines.
This paradigm blends IoT home automation with intuitive hubs to monitor conditions, adjust settings, and alert you in real time, delivering convenience, personalization, and heightened security. When you see lights dim at sunset, your thermostat learn your preferred comfort, and your camera notify you of unusual activity, you’re witnessing the core home automation benefits in action.
Choosing the Right Smart Home Devices for Your Ecosystem
Choosing the right smart home devices means understanding compatibility, standards, and future expandability. Look for devices that support open standards or the Matter protocol to improve interoperability across ecosystems, and balance a single-brand approach with cross-brand flexibility.
Assess your network backbone and security posture: a reliable Wi-Fi, a dedicated hub, and a plan for firmware updates protect your automation from lag and vulnerabilities. The result is a resilient setup that makes daily life feel seamless rather than clunky.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency with IoT and Smart Home Automation
Energy efficiency with IoT becomes a practical outcome when smart devices respond to occupancy, weather, and schedules. Smart thermostats, LEDs, and plugs optimize usage by turning off or dimming when spaces are empty or daylight reduces the need for artificial lighting.
These energy-conscious patterns translate into measurable cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint. By leveraging IoT home automation, you can orchestrate scenes that maximize energy efficiency with IoT while keeping comfort intact.
Security, Privacy, and Safe Practice in a Connected Home
Security and privacy should be integral from day one. Select devices with reputable security practices, enable automatic updates, and use strong passwords and two-factor authentication where available. Isolate smart devices on a guest or IoT network to limit exposure if a device is compromised.
Regularly review permissions, maintain segmentation, and keep a practical rollout plan to avoid overwhelming risk. A phased approach lets you learn how automation affects your home while maintaining control and visibility.
Starting Small: A Practical Roadmap to a Scalable Smart Home
Begin with a focused, expandable setup that demonstrates tangible benefits without complexity. A smart thermostat paired with adaptive lighting can noticeably improve comfort and energy use, while a smart lock adds everyday convenience and safety.
Map your daily routines to automation: morning wake-ups, leaving the house, and returning home. As you gain confidence, add devices that integrate smoothly with your existing ecosystem, prioritizing reliability, security, and interoperability.
The Future of Smart Homes: AI, Edge Computing, and Interoperability
The future of Smart Homes and IoT is likely to be more integrated, proactive, and intelligent, powered by AI, edge computing, and stronger sensor networks. These advances will enable devices to anticipate needs with greater accuracy and respond even during intermittent internet connectivity.
Expect richer data-driven experiences, faster local processing, and growing interoperability across brands and platforms. This evolving landscape will expand connected living capabilities, improve energy management, and enable more personalized, seamless user experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Smart Homes and IoT, and what home automation benefits do they offer?
Smart Homes and IoT blend internet-connected devices and sensors with a central hub to automate everyday tasks. The home automation benefits include convenience, energy savings, improved comfort, and enhanced security.
How do smart home devices contribute to energy efficiency with IoT?
Smart home devices such as thermostats, lights, and plugs adjust settings based on occupancy and weather, reducing energy use and lowering costs while maintaining comfort.
What does ‘connected living’ mean in the context of Smart Homes and IoT?
Connected living describes devices that communicate with each other and you in real time, enabling automated routines, proactive alerts, and a seamless daily experience.
What are the core components of a modern Smart Home and IoT system?
Key components include sensors, smart devices (thermostats, lights, cameras, locks, appliances), a hub or bridge for local automation, and a cloud service for remote access; many ecosystems support common standards like Matter for better compatibility.
How should I address security and privacy in a Smart Homes and IoT setup?
Prioritize reputable devices, enable firmware updates, use strong passwords, and segment your network. For IoT home automation, regularly review permissions and enable two-factor authentication where available.
What practical steps can I take to start building a connected Smart Homes and IoT system?
Begin with a small, expandable setup of compatible smart home devices, choose products that support Matter for cross-brand compatibility, ensure a reliable network or hub, and design scenes and routines that improve daily life and energy use.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Definition | Smart Homes and IoT connect devices and sensors through a centralized system, enabling communication, automation, monitoring, and real-time notifications to simplify daily life. |
| Core components | Sensors and smart devices, a hub/bridge for local routing, and cloud services for advanced processing and remote access; Matter supports cross-brand compatibility; emphasis on expandability. |
| What makes it practical | Beyond novelty: monitoring conditions, auto-adjustments, and timely alerts that save time, improve comfort, and reduce energy use. |
| Getting started | Start small and expandable with a few well-chosen devices; align automation with your routines; consider standards (e.g., Matter) and ensure a reliable network; prioritize security. |
| Practical examples | Smart thermostat with adaptive lighting; smart locks; voice assistants for reminders; morning routines; security cameras and sensors for monitoring. |
| Security & privacy | Choose reputable devices, enable firmware updates, use strong unique passwords, segment networks, review app permissions, and consider two-factor authentication. |
| Design & experience | Focus on seamless user experience, customizable scenes, single-app or voice control, and a mix of automation with manual control. |
| Future outlook | Advances in AI, edge computing, and sensors will drive more proactive, interoperable, and energy-management improvements across devices and platforms. |
Summary
Conclusion